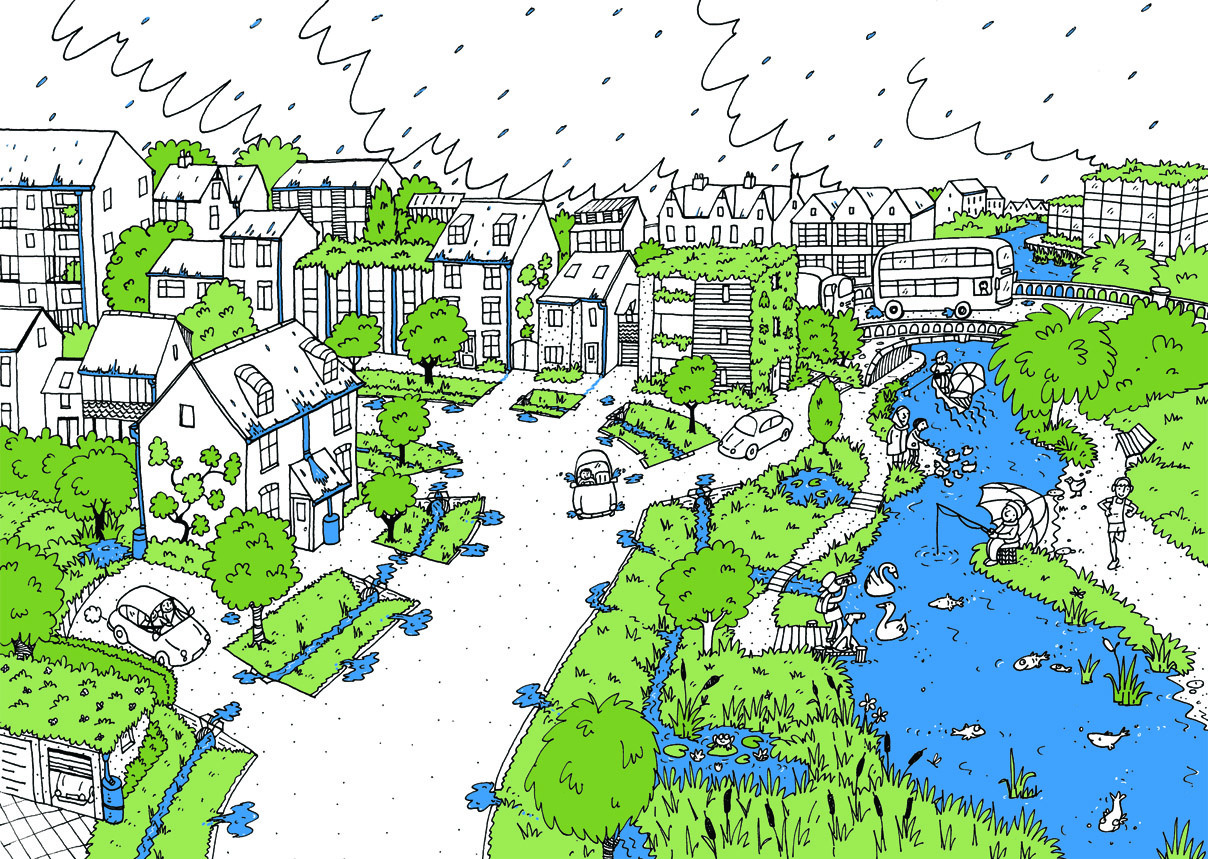
Az úgynevezett SuDs-okra a LIFE Városi Eső csapata mind a barcelonai, mind a berlini tanulmányi útján számos példát látott, a következőkben átvesszük, hogy mik azok a SuDsok és milyen előnyökkel rendelkeznek a városi esővízkezelés területén.
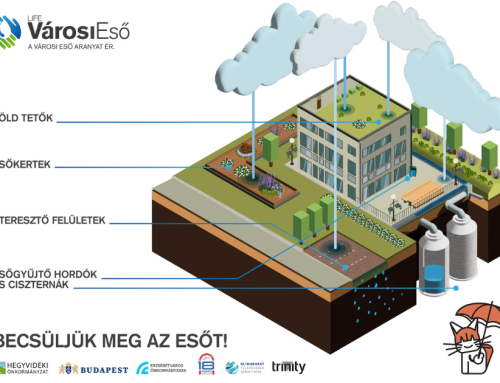
A fenntartható vízelvezető rendszerek (SuDS) olyan tervezett megoldások, amelyek a csapadékvizet a lehető legközelebb a forrásához kezelik, hogy utánozzák a természetes vízelvezetést, és elősegítsék annak beszivárgását, lassítását és passzív kezelését.
A SuDS rendszerek célja mind a városi lefolyásból eredő árvíz- és szennyezési kockázatok kezelése, mind pedig az ökológiai környezet javítása, illetve biodiverz területek kialakítása, ahol ez csak lehetséges. Ezért a SuDS rendszerek többfunkciósak és több előnyt is kínálnak, amelyeket mindig figyelembe kell venni a tervezés során.
A SuDS alapelvei szerint a beszivárgás és a lassítás mellett a rendszer lassú elvezetést is alkalmaz. Sok SuDS megoldás kombinálja a beszivárgást és a lassítást. Azokban az esetekben, amikor a beszivárgás nem lehetséges, például talajtípus vagy szennyeződés miatt, az inkább a lassítást alkalmazó SuDS rendszerek előnyben részesülnek.
A jó SuDS tervezés követi a SuDS filozófiát, amelynek alapelvei a következők:
- Vízkezelési lánc – több SuDS komponens sorba kapcsolása, területek kategorizálása földhasználat és vízelvezetés típus szerint.
- Csapadék kezelése helyben – a lehulló csapadékot a lehető legközelebb kell kezelni a attól a helytől számítva, ahol lehullott
- Víz kezelése a felszínen – a lefolyóvizet lehetőség szerint a felszínen kell kezelni.
- Korai bevatkozás – a SuDS használatát már az ingatlan kiválasztásának és tervezésének korai szakaszaiban figyelembe kell venni.
- Jó gyakorlat az lassító és lassú elvezetést alkalmazó SuDS rendszerek esetén, hogy felszíni jellegű elemeket használnak az alagsori tárolás helyett, és az elvezetési rendszert a katasztrofális árvizek átirányításával összehangolják.
Amikor SuDS rendszereket használnak közúti hálózattal vagy meglévő beépített területeken történő utólagos telepítéskor, a közúti vízelvezetés általában meghatározó tényező lesz a SuDS alakításában. Ez azért van, mert a közúti lefolyás gyakran nagy százalékban részt vesz a fejlesztett területekről lefolyó vízösszmennyiségben, és ez az a felületi vízrész, amely a legmagasabb szintű szennyező anyagot tartalmazza.
(magyar feliratkhoz válaszd a Beállítások–>Feliratok–>Automatikus fordítás–>magyar beállítást)
A SuDS rendszerek előnyei:
- Árvízkezelés – csökkenti az árvíz kockázatát .
- Vízminőség-kezelés – csökkenti a szétterjedt szennyezés hatását.
- Élmény- és biodiverzitás-javítás – a zöld infrastruktúra integrálása a SuDS megoldásokkal lehetőséget nyújt élőhelyek, rekreációs és biodiverzitás területek kialakítására.
- Vízkészletek – a SuDS hozzájárulhat a talajvíztartalékok feltöltéséhez és az esővíz újrahasznosításához.
- Közösségi előnyök – vonzó, jól kialakított közterületek, amelyekbe a SuDS is beépül, segíthetnek jobb közösségek kialakításában a társadalmi összetartás és az életminőség javítása révén.
- Rekreáció – többcélú SuDS elemek nemcsak a felületi vizeket kezelhetik, hanem sport- és játéktérként is szolgálhatnak.
- Edukáció – a SuDS nagyszerű edukációs lehetőséget kínál mind a gyerekek, mind a felnőttek számára, miközben rekreációs teret is biztosít
- Fejlesztés lehetővé tétele – a SuDS hozzájárulhat a már meglévő vízelvezetési hálózatok kapacitásának felszabadításához, és a SuDS biztosítása gyakran az építési engedély előfeltétele lehet.
A fordítás alapját a következő forrás képezi: Local Government Association
Kép forrása: Thames21.org





Hagyj üzenetet